What Is debt-to-income ratio? (+ how to improve it)
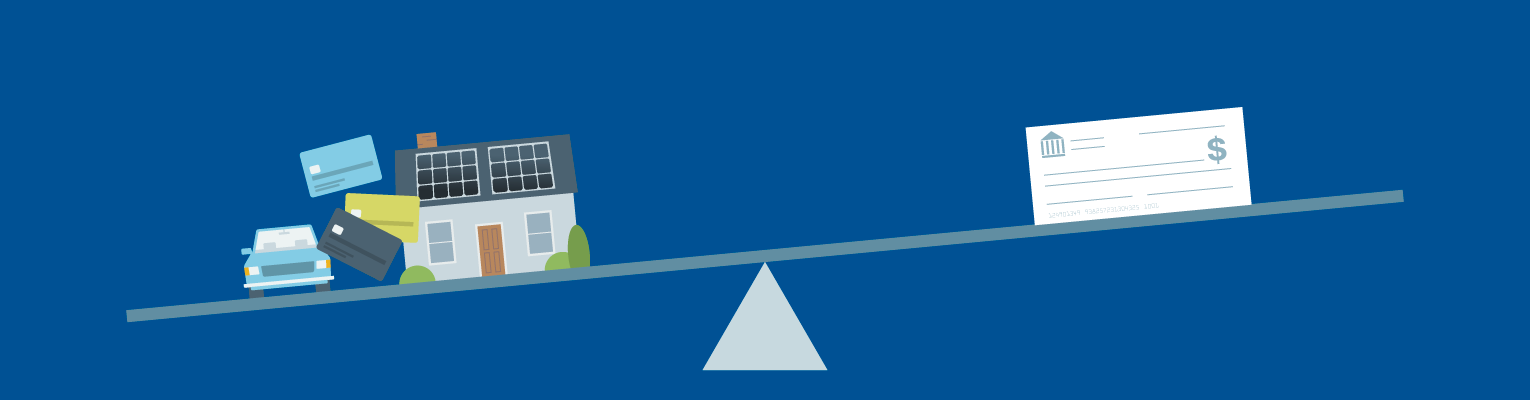
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is a comparison of your income to your current debt load and it plays a big factor in how lenders determine your borrowing risk.
When you apply for a personal loan or line of credit, lenders look at more than just your credit history and credit scores. They also want to know how much debt you’re carrying—and if you can comfortably afford to take on more. That’s where your debt-to-income ratio comes in.
What is debt-to-income ratio?
Your debt-to-income ratio compares your debt payments to your monthly gross income or how much you earn each month before taxes and other deductions. Your DTI ratio gives lenders a clearer picture of your current debt and income, and is used to determine how much money you can afford to borrow responsibly.
Examples of debt that lenders will consider:
Minimum credit card payments
Loan payments (such as car payments, student loan payments, personal loans, and other loan payments)
Monthly alimony or child support payments
Rent payment or mortgage payments
Other debts included in your credit report
Examples of debt lenders don’t consider:
Utilities like gas and electricity
Cable bills
Phone bills
Health insurance costs
Groceries
Entertainment and other variable expenses
Lenders typically divide your DTI ratio into two components: front-end DTI and back-end DTI.
Front-end DTI
Also known as a housing ratio, your front-end ratio includes housing expenses such as monthly mortgage payments, property taxes, monthly homeowner’s association dues, and homeowner’s insurance.
Back-end DTI
Your back-end ratio includes your front-end DTI plus all your other monthly DTI debt (credit card bills, car loan, etc.) While both are important, most lenders focus on your back-end DTI because it presents the most accurate account of your recurring monthly costs.
Remember, it's essential to be as accurate as possible when reporting your income to lenders. And don’t forget to include any income from bonuses or overtime pay. Most lenders verify income during the loan application process, so if your numbers differ from theirs, it can delay the process or cause your loan application to be declined.
Why is DTI ratio important?
Along with your credit history and credit score, DTI is one of the most critical measurements of your creditworthiness in the eyes of lenders. It helps them determine how responsible you are with your debt. Having a good DTI ratio matters for a few key reasons:
1. It can help with home buying.
Your DTI has a significant impact on your ability to take out a home loan. A DTI of 43%
is typically the highest ratio one can have to qualify for a mortgage, but mortgage lenders generally prefer that borrowers have a DTI of 36% or less.
2. It can help determine your approval for a personal loan.
When it comes to personal loans, lenders often look for borrowers with a DTI no higher than 40%. However, sometimes exceptions are made for borrowers with a higher DTI but generally good credit.
3. It can help you qualify for better interest rates.
If you’ve lowered your DTI since you last took out a loan, such as a personal or auto loan, you may be able to qualify for a lower interest rate through refinancing.
4. It provides a snapshot of your overall financial health.
If your DTI ratio is below 36%, it’s a pretty good indicator that you can take on and manage new debt responsibly. If your DTI is over 43%—and particularly if it’s over 50%—you’ll likely need to pay down some debt or find other sources of income before lenders will approve you for a mortgage or personal loan.
5. It works in tandem with your credit score.
Though your DTI does not directly impact your credit score, it is closely associated with your credit utilization. If your DTI and credit utilization ratios are both low, you’ll have a better chance of being approved for loans.
Keep in mind: most lenders do not advertise maximum debt-to-income ratios, but instead provide guidelines that offer some flexibility. For example, a common guideline is the 28/36 rule used by some lenders to assess borrowing capacity. According to this rule, a household should only spend 27% of its gross monthly income on housing expenses, and no more than 36% on debt expenses—like car payments and credit cards.
How to calculate debt-to-income ratio in 3 steps
Since lenders use your DTI to determine whether or not you’re capable of taking on more debt, it’s a good idea to know your DTI before you apply. Thankfully, the formula is pretty straightforward:
Step 1: Add up your total monthly debt payments.
Add up all recurring monthly payments that factor into your DTI.
Step 2: Divide that number by your gross monthly income.
Once you’ve totaled all your monthly debts, divide that number by your gross monthly income.
Step 3: Convert the total into a percentage.
Take the number you’ve just calculated and multiply it by 100 to get your final DTI ratio.
Debt to income ratio example:
Sarah wants to calculate her debt-to-income ratio before applying for a loan. Her monthly bills and income are as follows:
Rent: $1,200
Student loan: $400
Credit cards: $300
Gross income: $5,000
Sarah's total monthly debt payment is $1,900:
$1,900 = $1,200 + $400 + $300
Sarah's DTI ratio is 0.38:
0.38 = $1,900 ÷÷$5,000
In other words, Sarah has a 38% debt-to-income ratio.
How to lower your debt-to-income ratio
Like your credit score, there are a number of ways to improve your debt-to-income ratio. If your current DTI ratio is over 40% (or close to it), you can take a few different routes to improve it.
Pay down existing debt.
Increase the amount you’re currently paying on your monthly debt. Rather than making the minimum credit card or loan payment every month, pay off slightly more. Even a small increase will help decrease your overall debt and lower your DTI ratio as a result.
Avoid additional debt.
Focus on paying down your current debt without adding more recurring debt obligations.
Postpone large purchases.
If possible, avoid making large purchases that will use up a large portion of your available credit.
Create and stick to a budget.
If you don’t already have one, create a personal monthly budget and stick to it. Your budget can help you decrease monthly spending and increase monthly debt payments to pay down your existing debt faster.
Check your DTI ratio regularly.
Make a note to recalculate your debt-to-income ratio on the same day every month. Note any changes, record your progress, and use it for motivation.
The bottom line
The debt-to-income ratio is an important measurement used in the loan application and approval process. Understanding what it is, and what you can do to improve it, may help enhance your overall financial wellness and increase your ability to secure a future loan. To maintain a healthy DTI, keep paying as much as you can toward your debts each month.
Debt-to-income ratio FAQ
What is a good debt-to-income ratio?
Generally, lenders consider at or below 36% a good debt-to-income ratio, though many will lend to individuals with a higher ratio. For example, a DTI of 43% is the maximum debt to income a borrower can have for a qualified mortgage, but a DTI of 20% would be considered more favorable.
Is monthly rent included in debt-to-income ratio?
Whether or not rent is included in the debt-to-income ratio calculation depends on the type of loan you’re applying for. For a personal loan, any amount you pay toward housing such as rent counts toward your total monthly debt and will be included in calculating DTI. When applying for a mortgage, your current rental or lease payment is not included in your debt-to-income ratio calculation.
How can I lower my debt-to-income ratio quickly?
The quickest way to lower your debt-to-income ratio (besides getting a pay or salary increase) is to pay off more of your debt than the minimum required. There are a number of different strategies for paying off debt: the debt avalanche method will pay off debt the fastest, but look into the debt snowball and debt snowflake methods as well.
What are some other ways to lower my debt-to-income ratio?
In addition to paying more toward your debts, you should also avoid taking on more debt and avoid or postpone large purchases that will add to it. Finally, you can find ways to increase your monthly income, such as taking on a side hustle or selling unwanted items online.
You May Also Like




